Battery Cells and Stacks
Control Drying, Thickness & Conductivity in Battery Electrode Production
Consumer electronics, automotive, stationary and industrial applications require highly efficient energy storage solutions. Battery cell manufacturers have to ensure excellent quality while addressing high troughput specifications and finally maximizing the uptime of the equipment. Coating processes have to monitored, especially for manufacturing of:
- Current collectors
- Electrodes
- Anodes
- Cathodes
- Separators
- Electrolytes
Testing
- Sheet resistance
- Conductivity
- Functionalization
- Thickness
- Homogeneity
- Area weight
- Drying status
- Areal capacity
- Porosity
Applications
- Deposition process control
- Drying process control
- Calandering process control
- Welding process control
- Quality control
Substrates
- Metal foil (Cu, Al)
- Plastic foil (BOPP)
- Wafer
- Mesh
- Non-woven
- Ceramics
Processes
- S2S
- R2R
- Wafer level
Environment
- In-vacuo and ex-vacuo
- In-situ and ex-situ
- Inline and offline
- Wet and dry
Cathode Materials
- NMC (NCM) – Lithium Nickel Cobalt Manganese Oxide (LiNiCoMnO2)
- LFP – Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4/C)
- NCA – Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (LiNiCoAlO2)
- LMO – Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4)
- LNMO – Lithium Nickel Manganese Spinel (LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4)
- LCO – Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2)
Anode Materials
- Graphite
- Amorphous carbon
- Activated carbon
- Carbon black
- Conductive additives
- Graphene
Use Case Electrodes
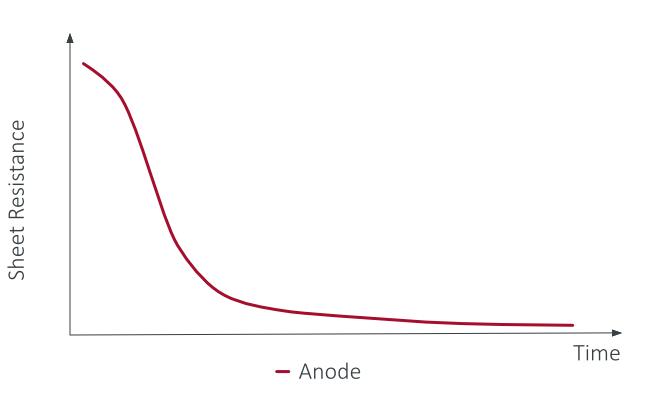
Drying Status
Areal Capacity
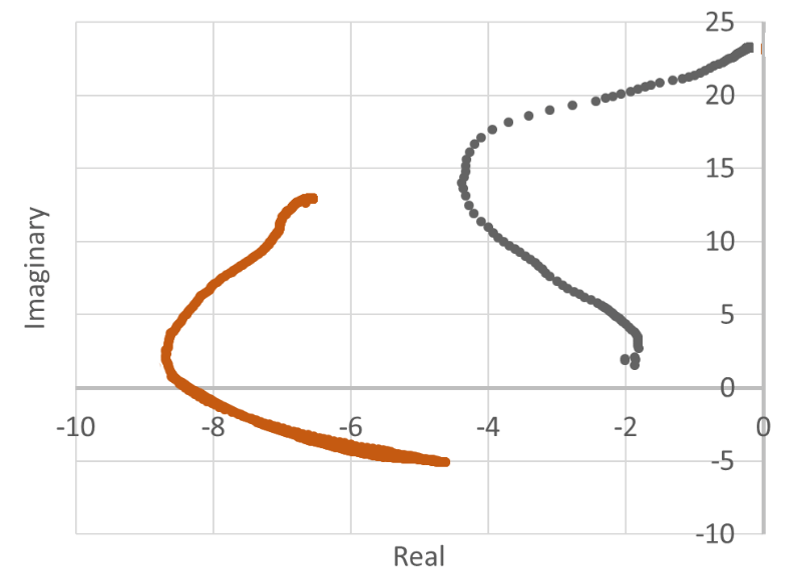
Drying status over time as well as areal capacities of electrode ink or pastes deposited on substrates were derived by complex eddy current impedance.
